迁移学习
简单来说迁移学习是把在 ImageNet 等大型数据集上训练好的 CNN 模型拿过来,经过简单的调整应用到自己的项目上去。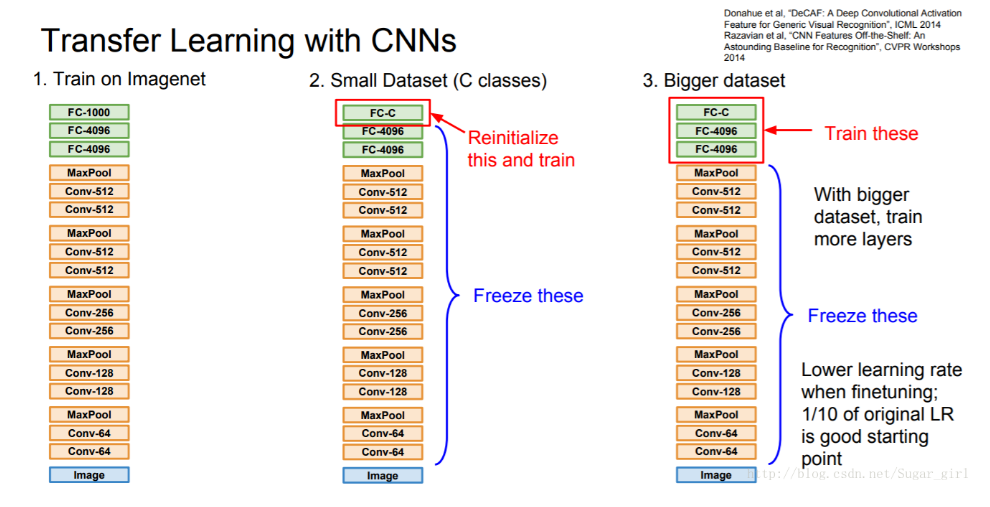
迁移学习的分类
迁移学习分为三种:
- 第一种叫 transfer learning。用于图像分类的卷积神经网络由两部分组成:从一系列卷积层和池化层开始,并以全连接的分类器结束。第一部分称为模型的卷积基(convolutional base),即全连接层之前的卷积池化部分,特征提取就是利用预训练好的的网络模型的卷积基,运行新的数据,并在输出之上训练一个新的分类器(见图 1.1)。因此,我们只需要训练分类器部分,卷积基直接用现成的不动。
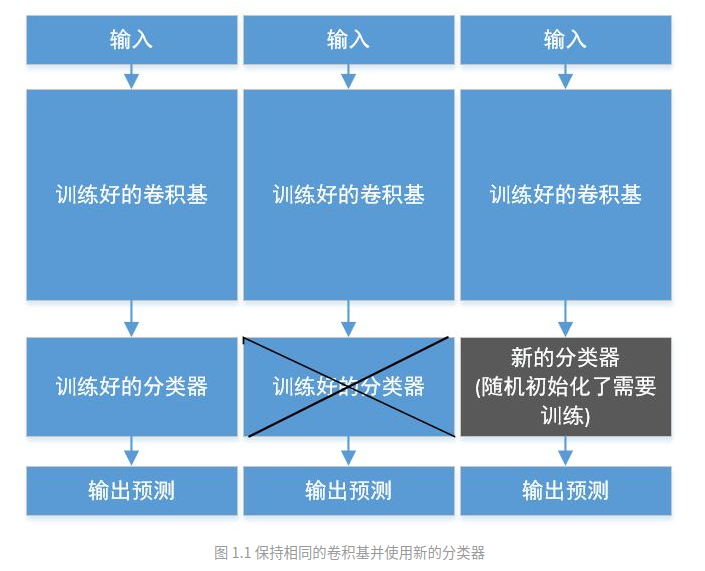
为什么只重用卷积基?能使用相同的分类器吗?一般来说前面的卷积基提取了低级特征,这在很多其他类似问题是可以通用的。而最后的全连接层是与具体问题相关的高级特征,因此不太可复用。 - 第二种是 fine tune,即微调,就是让一部分底层也参与训练。一般来说,只有在顶层的分类器已经被训练好之后,才去微调卷积基的顶层。
预训练模型。例如,Caffe 库有一个 model zoo,其他人可以在这里找到各种训练好的模型的 checkpoint。
一个典型的迁移学习过程是这样的。首先通过 transfer learning 对新的数据集进行训练,训练过一定 epoch 之后,改用 fine tune 方法继续训练,同时降低学习率。这样做是因为如果一开始就采用 fine tune 方法的话,网络还没有适应新的数据,那么在进行参数更新的时候,比较大的梯度可能会导致原本训练的比较好的参数被污染,反而导致效果下降。
微调经验总结
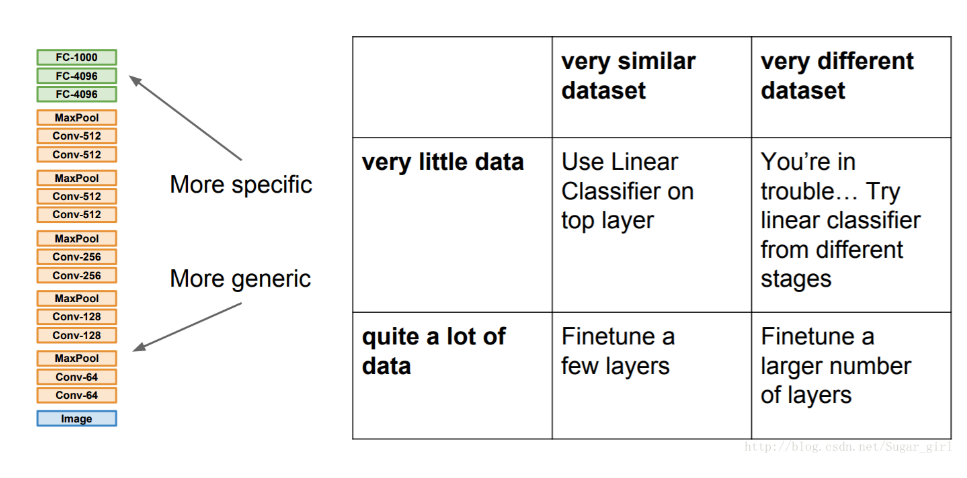
主要的因素是数据集的大小和原始数据集的相似性。有一点一定记住:网络前几层学到的是通用特征,后面几层学到的是与类别相关的特征。下面分情况讨论:
- 新数据集很小,与原始数据集类似。 因为新数据集比较小,如果 fine-tune 可能会过拟合;又因为新旧数据集类似,所以可能高层特征类似,可以使用预训练网络当做特征提取器,用提取的特征训练线性分类器。
- 新数据集很大,与原始数据集类似。 可以微调,不用担心过拟合。
- 新数据集很小但与原始数据集非常不同。 新数据集小,最好不要 fine-tune,和原数据集不类似,最好也不使用高层特征。这时可是使用前面层的特征来训练 SVM 分类器。
- 新数据集很大,与原始数据集非常不同。 因为新数据集足够大,可以重新训练。但是实践中 fine-tune 预训练模型还是有益的。新数据集足够大,可以 fine-tine 整个网络。
代码步骤
加载数据
这一步很正常,主要是处理图片数据和划分数据集加载 MobileNetV2 模型(不含全连接层)
Keras 的应用模块 Application 提供了带有预训练权重的 Keras 模型,这些模型可以用来进行预测、特征提取和 finetune。你可以从 keras.applications 模块中导入它。1
base_model = MobileNetV2(weights='imagenet', include_top=False)
添加新的顶层
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8def add_new_last_layer(base_model, nb_classes):
x = base_model.output
x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
# GlobalAveragePooling2D 将 MxNxC 的张量转换成 1xC 张量,C是通道数
x = Dense(FC_SIZE, activation='relu')(x)
predictions = Dense(nb_classes, activation='softmax')(x)
model = Model(input=base_model.input, output=predictions)
return model训练顶层分类器
冻结 base_model 所有层,然后进行训练。其实这一步也可以和上一步结合起来写,更加简洁:1
2
3
4
5
6def setup_to_transfer_learn(model, base_model):
for layer in base_model.layers:
layer.trainable = False
model.compile(optimizer='rmsprop', loss='categorical_crossentropy', metrics=['accuracy'])
setup_to_transfer_learn(model, base_model)1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10from keras import models
from keras import layers
# 在conv_base的基础上添加全连接分类网络
conv_base = MobileNetV2(weights='imagenet', include_top=False)
conv_base.trainable = False
model = models.Sequential()
model.add(conv_base)
model.add(layers.Flatten())
model.add(layers.Dense(256, activation='relu'))
model.add(layers.Dense(1, activation='sigmoid'))对顶层分类器进行 fine_tuning
冻结部分层,对顶层分类器进行 Fine-tune
Fine-tune 以一个预训练好的网络为基础,在新的数据集上重新训练一小部分权重。fine-tune 应该在很低的学习率下进行。
1 | def setup_to_finetune(model): |
这里可能比较疑惑的是NB_MobileNetV2_LAYERS_TO_FREEZE是多少呢,怎么找呢。方法是利用Pycharm的Debug功能,查看base_model.layers中的值。
当然也可以选择使用layer name来进行选择:
1 | conv_base.trainable = True |
总体代码
1 | from keras.applications import MobileNetV2 |

